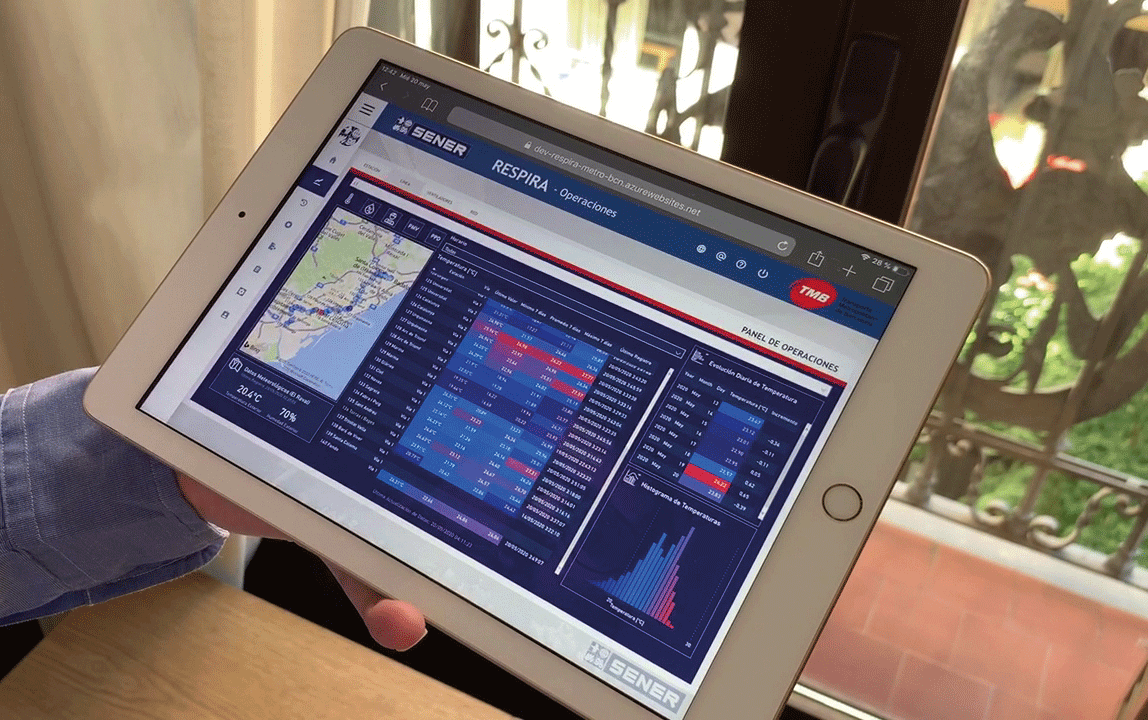
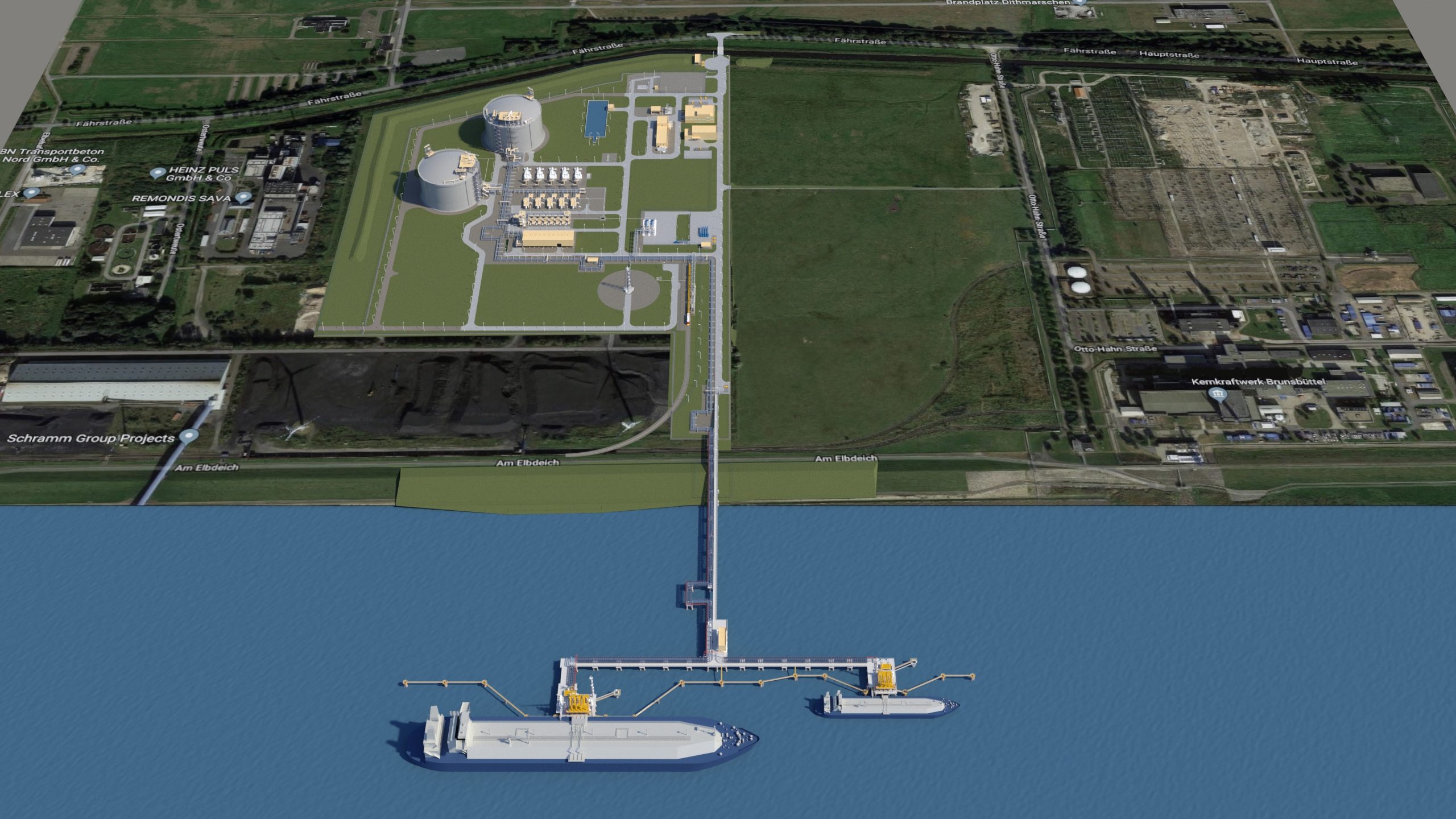
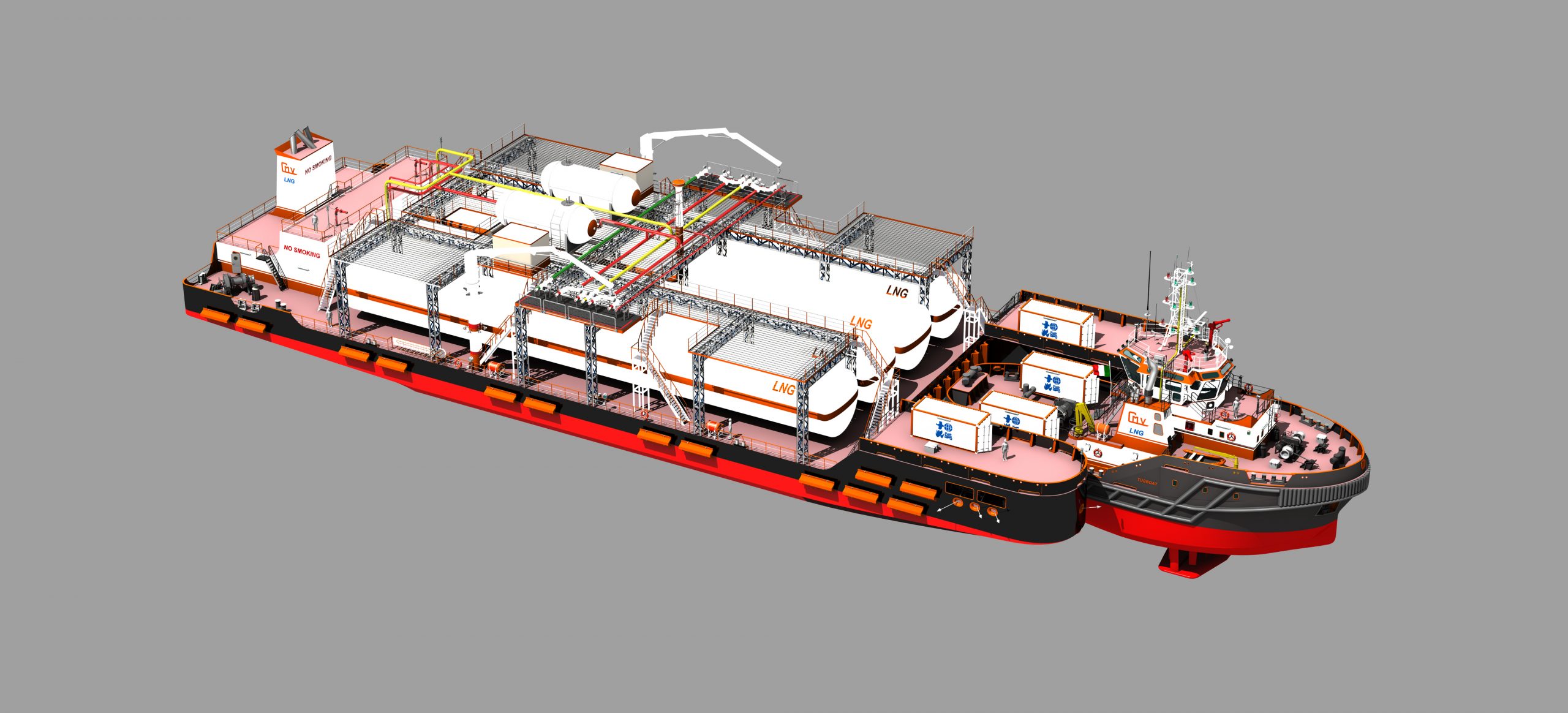
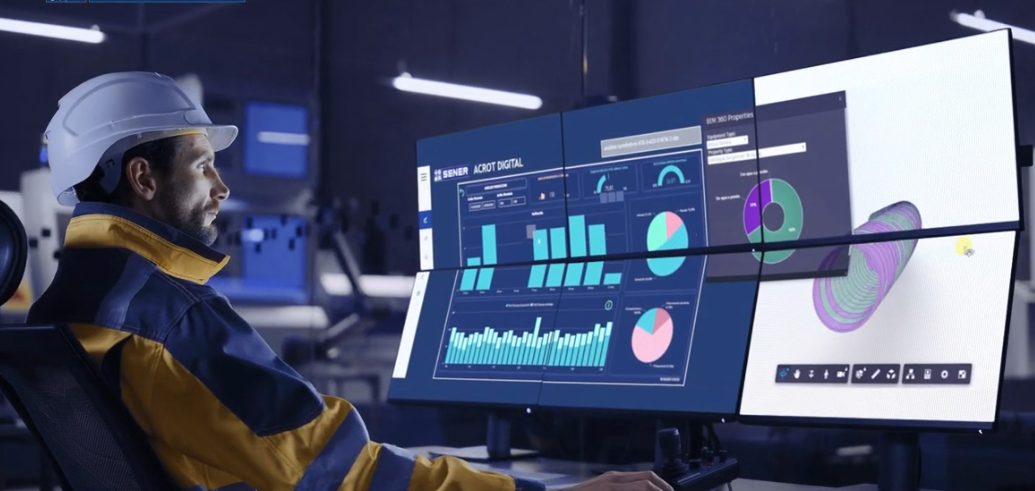
Artificial intelligence (AI) has moved beyond being a mere promise to become an essential tool in transforming industrial processes, driving a profound evolution in how operations are managed and optimised. Its impact extends across virtually all industrial sectors, enhancing operational efficiency, sustainability, and business competitiveness. Thanks to its ability to learn and analyse vast amounts of data in real-time, AI is revolutionising both internal operations and energy resource management, achieving greater efficiency and a direct impact on the sustainability and competitiveness of industries. This transformation is occurring at a time when companies are seeking to reduce costs, improve quality, and, most importantly, optimise their operations to meet market demands and the increasing pressure to reduce their carbon footprint.
The AI revolution in industry
Advancements in AI enable companies to tackle complex challenges, from process automation to optimising energy consumption. One of AI’s most significant contributions is its ability to identify hidden patterns and make recommendations based on historical and real-time data. This not only enhances decision-making but also minimises waste and optimises resource usage, leading to greater efficiency.
Moreover, AI can analyse various data sources (SCADA, MES, energy meters, and more) to identify areas for improvement. These intelligent models optimise not only energy consumption but also the “energy mix”—the combination of sources used in production. This directly impacts cost reduction and carbon footprint, helping companies comply with increasingly stringent sustainability and energy efficiency standards.
AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data generated by SCADA systems, MES platforms, and advanced sensors presents industries with an opportunity to significantly enhance efficiency. According to a Deloitte report, approximately 63% of manufacturing companies are already leveraging AI to optimise operations and cut production costs.
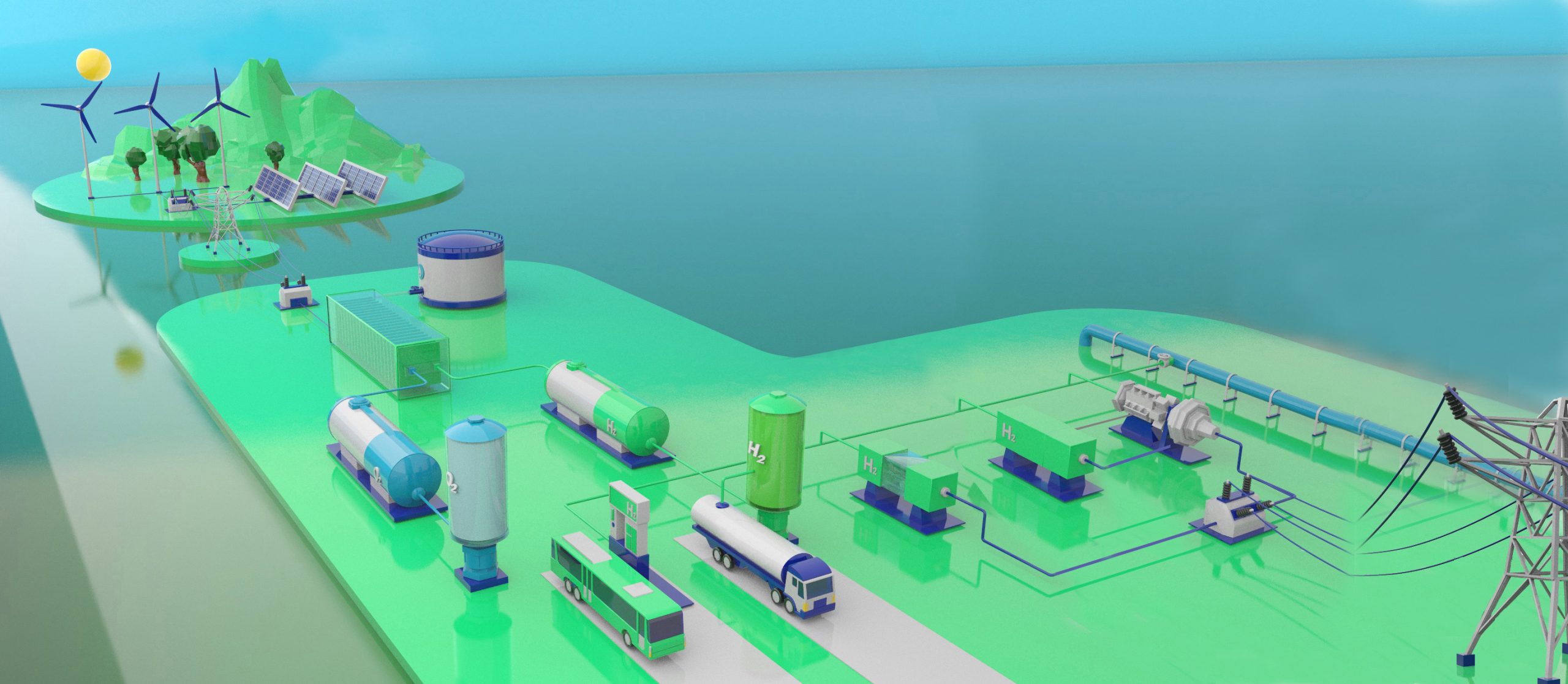
One of the most transformative aspects of AI in industry is energy optimisation. In an era of increasing demand for sustainable practices and carbon emission reductions, AI provides solutions for more efficient energy management. According to a report from the World Economic Forum, transitioning to low-carbon energy systems will require investments of between $92 trillion and $173 trillion by 2050, and AI can play a crucial role in improving the flexibility and efficiency of these systems, generating significant cost savings.
AI is instrumental in predicting energy demands, adjusting consumption based on market fluctuations, and improving the integration of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. These intermittent sources require precise and adaptive management, and AI enables more efficient coordination of energy distribution and storage, ensuring grid stability and reducing associated costs.
Artificial intelligence in industry has evolved beyond basic automation to more advanced technologies, such as deep learning and reinforcement learning. These enable industrial systems to respond to unexpected changes in real-time and continuously adapt to improve performance. According to McKinsey, this dynamic, real-time responsiveness allows for the optimisation of operational parameters to reduce waste and improve quality without requiring manual adjustments—achieving efficiency gains previously unattainable with traditional methods. For example, in consumer goods manufacturing, AI can automatically adjust the use of raw materials based on demand, reducing material waste.
Predictive maintenance: A paradigm shift
Predictive maintenance is one of AI’s most impactful applications in industry, enabling the prediction and prevention of equipment failures, thereby reducing downtime and repair costs. Unlike traditional preventive maintenance, which occurs at regular intervals regardless of equipment condition, AI-driven predictive maintenance uses real-time data analysis to forecast when a machine requires servicing.
According to McKinsey, this approach can reduce downtime by 50% and cut maintenance costs by 20%. This benefit is particularly significant in industries such as automotive manufacturing, where unplanned downtime can be extremely costly.
AI and Industry 4.0
The concept of Industry 4.0 is closely linked to AI adoption. The connectivity and real-time data analytics that define Industry 4.0 enable businesses to dynamically optimise their operations. Smart factories—where all production components are interconnected and controlled through AI—can automatically adjust to market needs or operational conditions.
One example of this evolution is mass customisation, an emerging trend in industries such as automotive manufacturing. AI models allow companies to flexibly adjust production, offering personalised products without significantly increasing costs. This ability to rapidly respond to market demands is crucial in an increasingly competitive environment. Additionally, AI facilitates the automation of previously manual or labour-intensive processes, not only improving efficiency but also freeing employees to focus on higher-value activities such as innovation and product development.
The adoption of AI has become a cornerstone of Industry 4.0, a revolution based on the interconnectivity of devices, data analytics, and advanced automation to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. In this ecosystem, interconnected devices continuously generate data, enabling AI models to identify inefficiencies and adjust processes in real-time to meet demand. According to a PwC report, Industry 4.0 could improve business operational efficiency by up to 20%, providing a crucial competitive advantage. By intelligently managing production, companies can significantly enhance their responsiveness to market changes and improve sustainability.
Energy optimisation and sustainability
In today’s sustainability-focused landscape, AI plays a crucial role in optimising energy consumption, which is not only essential for cost reduction but also for achieving sustainability goals. According to the World Economic Forum, transitioning to a low-carbon energy system is one of the most significant challenges of the coming decade, requiring massive investments to integrate AI technologies into energy management. For instance, an industrial plant can schedule equipment operation during off-peak hours, when energy is cheaper, or automatically adjust energy usage to avoid demand peaks.
Challenges and opportunities
The large-scale adoption of AI in industry faces several challenges. One of the main obstacles is existing digital infrastructure. Many industrial companies operate with legacy systems that are not designed to handle vast amounts of data or integrate AI technologies. Modernising these systems is essential for businesses to fully harness AI’s capabilities.
Despite AI’s clear benefits, its implementation presents challenges that companies must overcome to unlock its full potential. One of the biggest hurdles is upgrading technological infrastructure, as many businesses still rely on outdated systems that are not equipped for integration with advanced AI models. According to Boston Consulting Group, 70% of companies cite inadequate infrastructure and cultural resistance to change as the primary barriers to successful AI adoption in industry. Overcoming these challenges requires substantial investment in system upgrades and employee training, ensuring they can effectively collaborate with AI-driven tools.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is profoundly transforming industrial processes, providing solutions that enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and support sustainability goals. As industries advance towards the adoption of smarter technologies, those that effectively integrate AI will be in a leading position—capable of responding to evolving market demands and environmental challenges. The key to success lies in a strategic AI implementation, viewing it not merely as an automation tool but as an ally for innovation and sustainable growth.

 About us
About us